What are they and what do they do best.
Raster Images
In my last blog post about Image Resolution, I explained how images are made up of pixels if viewed on a screen or dots if printed. Any image made up from pixels is what is called a raster image. Photos are raster images, as are any JPEG, PNG or GIF image files for example.
Because they’re made up from pixels, raster images are subject to the limitations on resolution, in that low resolution images that are enlarged will lose quality and pixelate (see Image Resolution for more detail).
Raster images are usually, but not always, created in a camera and edited using software such as Adobe Photoshop. The larger the image size (pixel x pixel) and the larger the resolution (in pixels per inch, PPI) the larger the image file (in kilobytes, KB, or megabytes, MB).
Raster Pros & Cons
PROS:
- Rasters can depict a lot of detail at high resolutions, making them good for posters or brochures etc.
CONS:
- Raster images lose quality and pixelate if they have low-resolution or are enlarged too much.
- Raster images can end up with large file sizes, depending on the size of the image and how high its resolution.
Vector Images
Vectors images are human-designed computer-generated images, as opposed to raster images which can be created by cameras as well as by humans on computers. With vector images it's all about mathematics. The lines, shapes and gradients are all created in the computer using equations that calculate things like the curve between two points, angles between lines, and colour values for gradients etc. This numerical information is then plotted on a grid and rendered on the screen as an image.
This means that a vector image can be enlarged or reduced to any size without any loss of quality. Common vector image formats include EPS and SVG, and are often created and edited using software such as Adobe Illustrator.
IMPORTANT NOTE: A vector image can be easily converted into a raster image by resaving it as a raster file format, e.g. JPEG. This process then means the new image is subject to the same limitations as a raster image and the process is irreversible, so make sure you don’t lose or somehow overwrite your original vector file!
A raster image, on the other hand, cannot be simply converted into a vector image. The only way to do this is to redraw the raster image which is highly likely to be time consuming depending on the level of detail required.
Vector Pros & Cons
PROS
- Vector images do not lose quality when enlarged, making them the ideal format for logos, for example, which need to be scalable from a small format like a website icon, to a large format such as a banner or sign.
- Vector image files are generally small, relative to raster image files.
CONS
- It is very difficult to get photographic quality detail in a vector image.
NOTES FOR CLIENTS
LOGOS
When asking a graphic designer for a logo, make sure you ask for vector file formats, e.g. EPS, as well as raster ones, e.g. JPG, so that you have the most flexibility over how you can use your logo and what size you can cleanly scale it to.
PHOTOGRAPHY
Raster images, like photographs e.g. JPGS/PNGS, are only really useful to your graphic designer if they have high resolution. Otherwise your designer will be limited with how they can use and enlarge your images. So if you every get photographs taken of your products or services always make sure you receive high resolution images from any photographer you use and keep these safe!
TL:DR SUMMARY
Logos should always be created as vector images.
Rasters/photos are primarily only useful if high resolution.
This photo is a PNG raster image.
This closeup shows the tiny squares of colour (pixels) that make up the image.
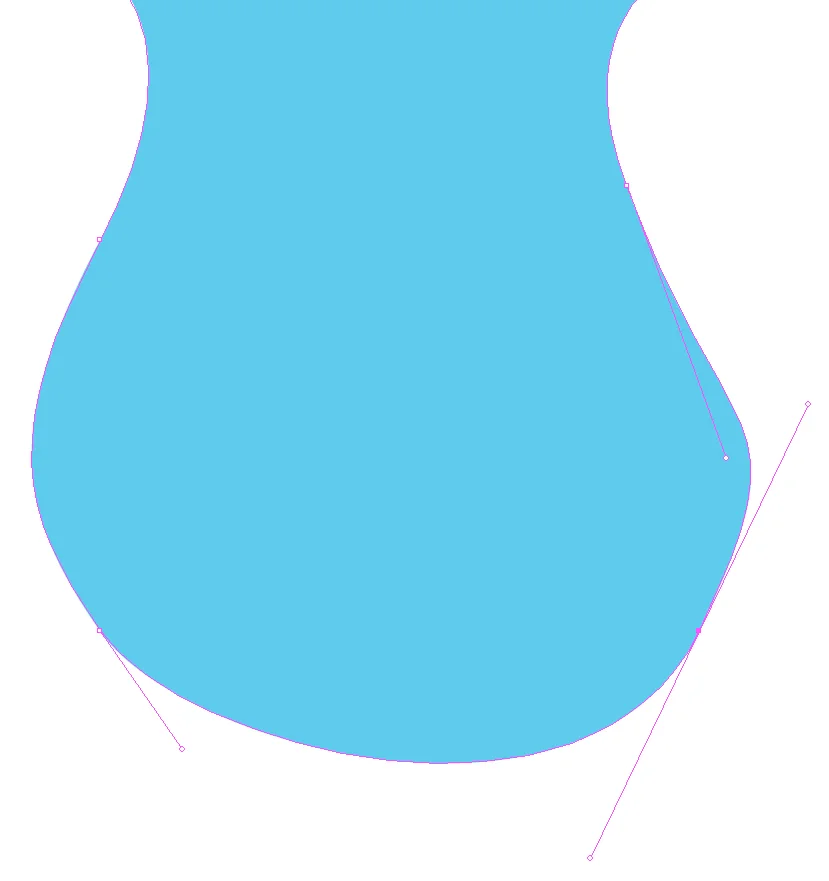
This is a vector drawing of a puzzle piece.
The image is made from lines, angles and mathematics. This means it can be scaled to up or down without losing image quality.
GLOSSARY
LOSSY COMPRESSION
Irreversible data compression that reduces data size at the expense of accuracy and quality.
LOSSLESS COMPRESSION
Reversible data compression that does not compromise on data accuracy and quality.
JPEG or JPG
A lossy raster file format. Typically smaller file sizes but variable in quality, especially for print. JPEG stands for Joint Photographic Experts Group - the name of the group who created this file format.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
A lossless raster file format of typically higher quality.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
A lossless raster file format that also supports low-resolution film clips and small animations.
EPS (Encapsulated PostScript)
A lossless document with a relatively small files size that can describe/output an vector image/drawing when opened/read by a computer program.
SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics)
A lossless text file that can be edited with any text editor but also output a vector image/drawing.